Rare Oncology News
Advertisement
Spotlight On
Chordoma
A chordoma is a rare type of cancerous bone tumor that can occur at any part of the spine or in the skull
Prevalence
Age of Onset

ICD-10
C76.7
Inheritance
Autosomal dominant

Autosomal recessive

Mitochondrial/Multigenic

X-linked dominant

X-linked recessive

Rare View
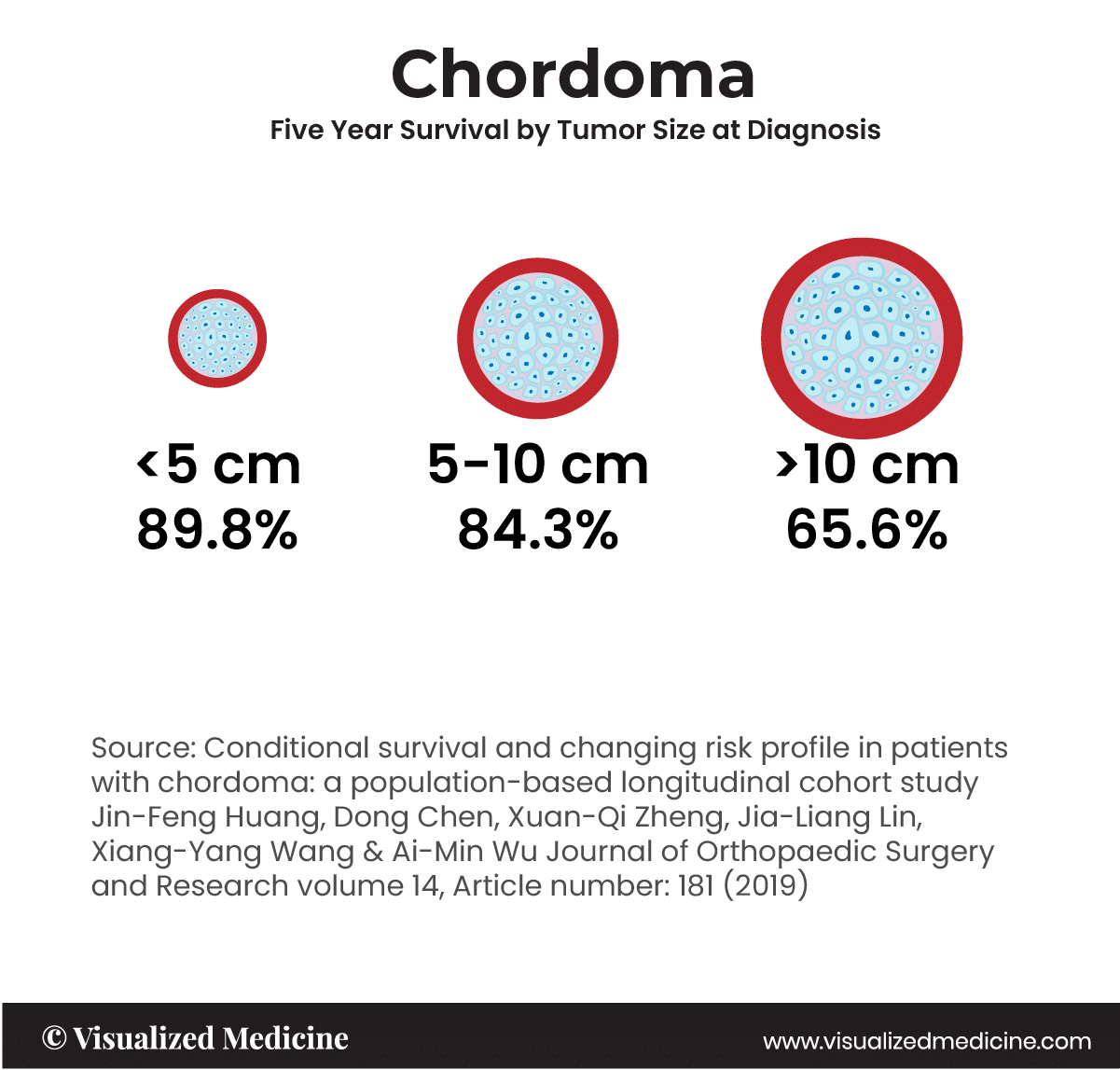
A chordoma is a rare type of cancerous tumor that can occur anywhere along the spine, from the base of the skull to the tailbone. Chordomas grow slowly, gradually extending into the bone and soft tissue around them. The tumors that arise from embryonic notochordal remnants along the length of the neuraxis at developmentally active sites. The median survival in the United States is about 7 years, with overall survival rates of ~68% at 5 years and ~40% at 10 years. Tumor size and disease stage can influence conditional survival for patients with chordoma.†
5 Facts you should know
FACT
A rare slow-growing neoplasm thought to arise from cellular remnants of the notochord
FACT
Chordomas typically present in adults between the ages of 40 and 70 and can occur anywhere along the spine
FACT
About half of all chordomas occur in the sacrum; about one third occur in the clivus
FACT
A chordoma that occurs at the base of the spine may cause problems with bladder and bowel function
FACT
The annual incidence of chordoma is approximately 1 in one million (300 new patients each year)
Interest over time
Google searches
Common signs & symptoms
Abnormality of the head
Head abnormality
Autosomal dominant inheritance
Abnormality of the vertebral column
Abnormality of the spine
Current treatments
Chordomas are treated with surgery because these tumors continuously grow, although they grow slowly. If the chordoma is not removed, it may wear away the bone and adjacent soft tissue, causing destruction of surrounding tissues.[4] The surgery aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible. The extent of the surgery, or the amount of tumor that may be removed, depends on the location of the tumor and how close it is to critical structures in the brain. In some cases, surgery is followed by radiation therapy to destroy any cancer cells that may remain after surgery, especially when the tumor cannot be removed completely.[5] Several studies have shown that carbon ion therapy or proton beam radiation may control tumor growth and improve survival.[6]
Radical resections of tumors (removal of all the tumor) with clean margins (with no remaining of the tumor) are associated with a longer period of being disease-free. If the tumor cannot be removed completely, because of the location and closeness to critical delicate structures, the addition of radiation therapy decreases the recurrence of the tumor. Frequent follow-up is needed because of the high rate of recurrence of these tumors. Tumor recurrence identified early is easier to treat. The time in between follow-up visits, including repeat MRI or CT scans, depends on the completeness of the resection. Because residual tumor shortens the recurrence time, patients with known or suspected residual tumor need to be evaluated more frequently.[4]
Top Clinical Trials
| Title | Description | Phases | Status | Interventions | More Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proton Beam Therapy for Chordoma Patients | The goal of this clinical research study is to learn if proton beam therapy, with or without photon beam radiation therapy, is effective in the treatment of skull base chordoma. | Phase 2 | Active, not recruiting | Radiation: Proton Beam Therapy|Radiation: Photon Beam Therapy | More Info |
| Nivolumab and Relatlimab in Treating Participants With Advanced Chordoma | This phase II trial studies how well nivolumab and relatlimab work in treating participants with chordoma that has spread to other places in the body. | Phase 2 | Recruiting | Biological: Nivolumab|Biological: Relatlimab | More Info |
| BN Brachyury and Radiation in Chordoma | The goal of this study is to determine if the combination of BN-Brachyury plus radiation therapy can induce objective radiographic response rate (ORR) in patients, using a Simon 2-stage optimal design. In stage 1, a minimum of threshold of activity will be needed to proceed to stage 2. | Phase 2 | Active, not recruiting | Biological: BN-Brachyury plus radiation | More Info |
| Talimogene Laherparepvec, Nivolumab and Trabectedin for Sarcoma | This is a Phase 2 study using talimogene laherparepvec, nivolumab, and trabectedin as first, second or third line therapy for advanced sarcoma, including desmoid tumor and chordoma. | Phase 2 | Recruiting | Drug: Talimogene Laherparepvec [IMLYGIC]|Drug: Nivolumab |Drug: Trabectedin | More Info |
| Study of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Children and Young Adults With INI1-Negative Cancers | This clinical trial is studying two immunotherapy drugs (nivolumab and ipilimumab) given together as a possible treatment for INI1-negative tumors. | Phase 2 | Recruiting | Drug: Nivolumab|Drug: Ipilimumab | More Info |
| A Phase 1/2 Safety Study of Intratumorally Dosed INT230-6 | Phase 1|Phase 2 | Recruiting | Drug: INT230-6|Biological: anti-PD-1 antibody|Biological: anti-CTLA-4 antibody | More Info | |
| Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Treating Patients With Rare Tumors | This study evaluates the intratumoral administration of escalating doses of a novel, experimental drug, INT230-6. Sponsor also plans to test INT230-6 in combination with anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies. | Phase 2 | Recruiting | Procedure: Biospecimen Collection|Biological: Ipilimumab|Biological: Nivolumab | More Info |
| A Phase II, Multicenter Study of the EZH2 Inhibitor Tazemetostat in Adult Subjects With INI1-Negative Tumors or Relapsed/Refractory Synovial Sarcoma | This is a Phase II, multicenter, open-label, single arm, 2-stage study of tazemetostat 800 mg BID (twice daily) and 1600 mg QD (once daily). | Phase 2 | Recruiting | Drug: Tazemetostat | More Info |
| Intravenous TAEK-VAC-HerBy Vaccine Alone and in Combination Treatment in HER2 Cancer Patients | A Phase 1/2 open label trial of intravenous administration of TAEK-VAC-HerBy vaccine in patients with advanced HER2- expressing cancer. | Phase 1|Phase 2 | Recruiting | Biological: TAEK-VAC-HerBy | More Info |
Top Treatments in Research
| Agent | Class/Mechanism of Action | Development Status | Company | Clinical Studies | More Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proton Beam Therapy|Radiation: Photon Beam Therapy | Photon Beam Therapy | Phase 2 | MD Anderson Cancer Center | More Info | More Info |
| Biological: Nivolumab|Biological: Relatlimab | Nivolumab is a human recombinant monoclonal immunoglobulin G4 antibody to the programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1) which has distinctive immunomodulatory activity and is used in cancer immunotherapy. Relatlimab (RELA), a human IgG4 LAG-3-blocking antibody, restores effector function of exhausted T cells | Phase 2 | Sponsor: Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center Collaborator: Bristol-Myers Squibb | More Info | More Info |
| Biological: BN-Brachyury plus radiation | Brachyury is highly expressed in all cells in nearly every chordoma tumor. Knock down of brachyury in chordoma cell lines induces growth arrest and apoptosis. BN-Brachyury utilizes a prime-boost vaccination regimen that has been optimized to include the gene for brachyury and other molecules known to increase immune activation. | Phase 2 | Bavarian Nordic | More Info | More Info |
| Drug: Talimogene Laherparepvec (IMLYGIC) |Drug: Nivolumab|Drug: Trabectedin | Talimogene laherparepvec (TVEC) is a type I herpes simplex virus genetically modified to preferentially replicate in tumor cells, enhance antigen loading of MHC class I molecules and express granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to increase tumor-antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Nivolumab is a human recombinant monoclonal immunoglobulin G4 antibody to the programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1) which has distinctive immunomodulatory activity and is used in cancer immunotherapy. Trabectedin is classified as an alkylating agent. | Phase 2 | Sarcoma Oncology Research Center, LLC | More Info | More Info |
| Nivolumab|Drug: Ipilimumab | Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system. | Phase 2 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | More Info | More Info |
| Drug: INT230-6|Biological: anti-PD-1 antibody|Biological: anti-CTLA-4 antibody | INT230-6 is a formulation consisting of a proprietary amphiphilic cell penetration enhancer molecule, 8-((2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino)octanoate, also referred to as SHAO, combined with cisplatin and vinblastine. | Phase 2 | Intensity Therapeutics, Inc. | More Info | More Info |
| Biological: Ipilimumab|Biological: Nivolumab | Nivolumab is a human recombinant monoclonal immunoglobulin G4 antibody to the programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1) which has distinctive immunomodulatory activity and is used in cancer immunotherapy. Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system. | Phase 2 | National Cancer Institute (NCI) | More Info | More Info |
| Tazemetostat | Tazemetostat is a first-in-class, small molecule enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) inhibitor. | Phase 2 | Epizyme, Inc. | More Info | More Info |
| Biological: TAEK-VAC-HerBy | TAEK-VAC-HerBy vaccine may induce a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL)-mediated immune response against tumor cells expressing the HER-2/neu antigen, which may result in the inhibition of proliferation in Her-2/neu-expressing tumor cells. | Phase 2 | Bavarian Nordic | More Info | More Info |
† Medline Plus, National Library of Medicine